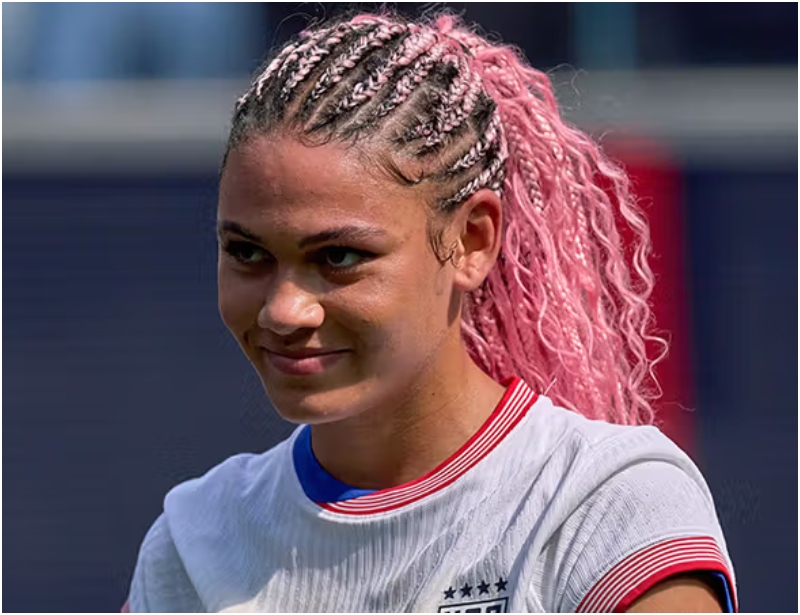
U.S. soccer star Trinity Rodman has become the highest-paid female footballer in the world after signing a new three-year contract with the Washington Spirit.
The signing represents a landmark deal that has both celebrated progress in women’s sports and ignited debate across the United States and beyond.
While the agreement secures one of the National Women’s Soccer League’s (NWSL) brightest talents, it has also exposed long-running tensions over salary caps, player rights, and how women’s football should balance financial growth with competitive fairness.

What makes Rodman’s deal historic?
Rodman, 23, an Olympic gold medallist with the U.S. women’s national team, agreed to remain with the Washington Spirit following months of speculation about a possible move to Europe.
Although the club did not officially disclose financial terms, the deal is widely reported to be worth more than $2 million per year, including bonuses, shattering the previous global wage record for a female footballer.
Washington Spirit owner Michele Kang described the contract as one of the most significant in women’s football history, saying it reflects Rodman’s “elite status” and the club’s ambition to serve as a global standard-bearer for the women’s game.
Why did the deal become controversial?
The controversy stems from the NWSL’s strict salary cap, which is set at $3.5 million per team for the 2026 season. Rodman’s salary alone accounts for a large portion of that cap, raising questions about whether the league’s financial rules limit teams’ ability to retain top talent—especially as European clubs, which do not operate under similar caps, continue to attract elite U.S. players.
Earlier negotiations between Rodman and the Spirit reportedly produced a contract that both sides believed complied with league rules. However, the NWSL rejected the agreement, with Commissioner Jessica Berman reportedly arguing that it violated the “spirit” of the salary cap regulations.
How did players respond?
The league’s rejection of the initial deal triggered a formal response from the NWSL Players Association (NWSLPA), which filed a grievance claiming the decision violated Rodman’s free agency rights and breached the collective bargaining agreement.
Tensions escalated further when the NWSL introduced a new “High Impact Player” mechanism, allowing teams to exceed the salary cap by up to US$1 million to sign or retain elite players based on criteria such as national team appearances or Ballon d’Or consideration.
The NWSLPA challenged the rule, arguing that the league had no authority to unilaterally alter player compensation structures without negotiation, potentially violating federal labour law.
How was the dispute resolved?
Despite the legal disputes, the Washington Spirit confirmed that the High Impact Player rule was factored into Rodman’s final contract. Club officials said the ongoing grievances would not affect her deal, allowing the forward to remain in the NWSL while still earning a world-record salary.
Why does this matter beyond the U.S.?
Rodman’s deal has global implications. On one hand, it sets a new benchmark for pay in women’s football, strengthening arguments for greater investment in the women’s game worldwide. On the other, it highlights structural challenges in leagues that rely on salary caps to maintain parity but risk losing star players to better-paying markets.
For African audiences and emerging football nations, the debate mirrors broader questions about how women’s sports can grow sustainably while fairly rewarding elite talent.
Rodman’s legacy and personal journey
Rodman, the daughter of former NBA star Dennis Rodman, was drafted at just 18 in 2021 and won NWSL Rookie of the Year as the Spirit claimed their first league title. She has since earned 47 caps and scored 11 goals for the U.S. national team.
Speaking at the announcement of her new deal, Rodman said she was focused on legacy rather than money, describing Washington as central to her personal and professional growth.
As women’s football continues to expand globally, Trinity Rodman’s contract may be remembered not only as a financial milestone, but as a turning point in how the sport negotiates value, fairness, and future growth.